Open
Categories
Recent Posts
When it comes to choosing the right diaper for your baby, understanding its structure can be a game - changer. A diaper is not just a simple piece of absorbent material; it's a carefully engineered product designed to keep your baby dry, comfortable, and rash - free. Let's take a closer look at the key components that make up a typical diaper.
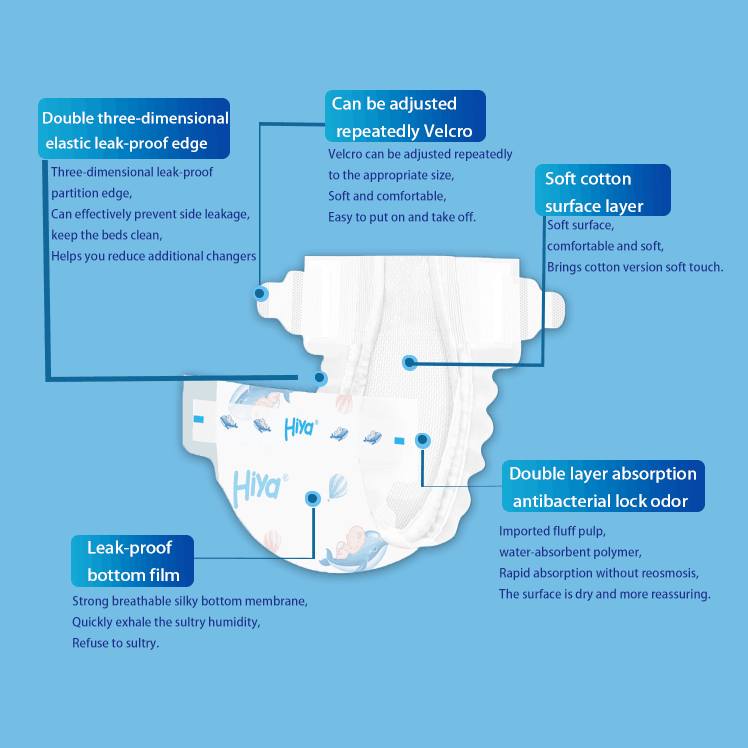
Function: Its primary role is to quickly transfer urine away from the baby's skin. The non - woven fabric allows for rapid absorption, preventing the skin from being in prolonged contact with moisture. This is crucial in reducing the risk of diaper rash. Some high - end diapers even have an additional feature in this layer, such as a wetness indicator. This is a small strip, typically yellow in color, that changes to blue or green when the diaper is wet. It provides a convenient way for parents to know when it's time for a diaper change, especially during the night or when the baby can't communicate yet.
Function: This layer is responsible for capturing, storing, and locking away urine. Once the urine passes through the inner layer, the fluff pulp initially spreads it out. Then, the SAP kicks in, rapidly absorbing the liquid and turning it into a gel - like substance. This not only prevents leaks but also ensures that the surface of the diaper remains dry to the touch. The quality and quantity of the absorbent core materials directly impact the diaper's overall performance. For example, a diaper with a higher proportion of high - quality SAP will have better absorbency and can last longer between changes.
Function: This layer, also known as the "acquisition layer" or "distribution layer", helps to evenly spread the urine across the absorbent core. It ensures that the absorbent core is utilized efficiently, preventing the formation of concentrated wet spots. By distributing the liquid evenly, the diaper can maintain its integrity and absorbency for a longer period. This is particularly important for active babies, as their movements can cause urine to pool in certain areas. The distribution layer helps to counteract this, ensuring that the diaper remains effective throughout the day.
Function: The outer layer's main function is to prevent any leakage of urine or feces from the diaper. The waterproof PE film acts as a barrier, keeping the liquid inside the diaper. At the same time, the non - woven fabric on the outer surface ensures that the diaper is not only leak - proof but also comfortable to wear. It prevents the diaper from feeling plasticky or causing irritation to the baby's skin through the clothes. Additionally, some diapers have elasticized leg cuffs and waistbands. These are made of stretchy materials and are an important part of the outer layer. The elasticized leg cuffs, often referred to as "leak guards", fit snugly around the baby's thighs, preventing any side leakage. The elasticized waistband provides a secure and comfortable fit around the baby's waist, allowing for movement while maintaining the integrity of the diaper.
Function: The fastening system is crucial for ensuring that the diaper stays in place on the baby. The adhesive tabs or hook - and - loop fasteners allow for easy adjustment of the diaper's tightness. This is important as babies come in different sizes and shapes, and their sizes change rapidly. The fastening system should be strong enough to keep the diaper secure during the baby's movements, whether it's crawling, walking, or just squirming around. At the same time, it should be easy to open and close, especially during diaper changes. Some diapers even have multiple adjustment points on the tabs, allowing for a more customized fit.
 fjxingyuan
fjxingyuan
 Linda@fjxingyuangroup.com
Linda@fjxingyuangroup.com
 360391852
360391852
 +86-595-85922600
+86-595-85922600
 +86-13514004600
+86-13514004600
 Scan our WeChat
Scan our WeChat

